This post will share an example to run the three volatility terminal commands including pslist, pstree and psscan
Before I proceed ahead,I would assume that you have installed volatility in your Linux system(in my case I am using UBUNTU,Installation explained at my earlier post at http://anupriti.blogspot.in/2015/09/volatility-advanced-memory-forensics.html) and you have a RAM dump of the OS u desire to analyse.In my case here I have taken the RAM dump of a Windows 7 OS as explained here at http://anupriti.blogspot.in/2015/09/volatility-command-using-imageinfo-to.html
Usage as follows :
pslist
The command pslist will be useful for any forensic prelim inquiry to find out the processes being run on the pc at the likely time of incident.The pslist command is used to list the processes of a system and it does not detect hidden or unlinked processes."pslist" module utilizes the same algorithm as the tasklist command that would be executed on the live computer. And also, Windows Task Manager uses the same approach as well.The command "pslist" traverses the list of active process structures that the Windows kernel maintains.The screen shot below shows a task manager activity of a windows PC i am using for test.Subsequently I have taken a fresh dump at this time and then analysed this dump with volatility on UBUNTU to find the process details which actually come out as the same as seen in the screenshots below :
 |
| Windows TASK MANAGER as seen in Windows OS (CLICK TO ENLARGE) |
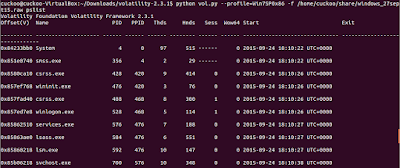
The command usage at terminal syntax goes like this :
vol.py --profile=Win7SP0x86 -f windows_memory.raw pslist
 |
| Click on image to ENLARGE |
 |
| Click on image to ENLARGE |
 |
| Click on image to ENLARGE |
The columns display the offset, process name, process ID, the parent process ID, number of threads, number of handles, and date/time when the process started. The offset is a virtual address by default, but the physical offset can be obtained with the -P switch as seen in the command below with screenshot.
vol.py --profile=Win7SP0x86 -f windows_memory.raw pslist -P
 |
| (Output with -P Switch) Click on image to ENLARGE |
pstree
pstree command is used to view the process listing in tree form and enumerates processes using the same technique as pslist, so it will also not show hidden or unlinked processes. Child process are indicated using indention and periods.SCreen shot of output and syntax as below :
vol.py --profile=Win7SP0x86 -f windows_memory.raw pstree
 |
| Click on image to ENLARGE |
psscan
psscan is used to enumerate processes by pool tag scanning and can find processes that previously terminated (inactive) and processes that have been hidden or unlinked by a rootkit. Syntax and screenshot of output as follows:vol.py --profile=Win7SP0x86 -f win7.dmp psscan
 |
| Click on image to ENLARGE |
 https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9097-2246
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9097-2246


















